Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that primarily affects the scalp, causing scaly patches, redness, and persistent dandruff. It often targets oily areas like the face, eyebrows, and chest, but it’s not limited to these areas. Despite its discomfort, it’s not contagious and doesn’t lead to permanent hair loss.
While seborrheic dermatitis may clear up on its own, it might require the long-term use of medicated shampoos or other treatments to manage symptoms and prevent future flare-ups.
This condition is known by various names, including dandruff, seborrheic eczema, and seborrheic psoriasis. In infants, it’s referred to as cradle cap.
Is seborrheic dermatitis bacterial or fungal?
Seborrheic dermatitis is primarily considered a fungal condition rather than a bacterial one. The main culprit implicated in seborrheic dermatitis is a type of yeast called Malassezia. This yeast is naturally present on the skin and is normally harmless. However, in individuals with seborrheic dermatitis, there tends to be an overgrowth of Malassezia, which can lead to irritation and inflammation of the skin, resulting in the characteristic symptoms of the condition.
Although bacteria can play a secondary role in seborrheic dermatitis by contributing to the inflammation and infection of affected areas, the primary trigger is the overgrowth of Malassezia yeast. Therefore, antifungal treatments are often more effective than antibacterial ones in managing seborrheic dermatitis.
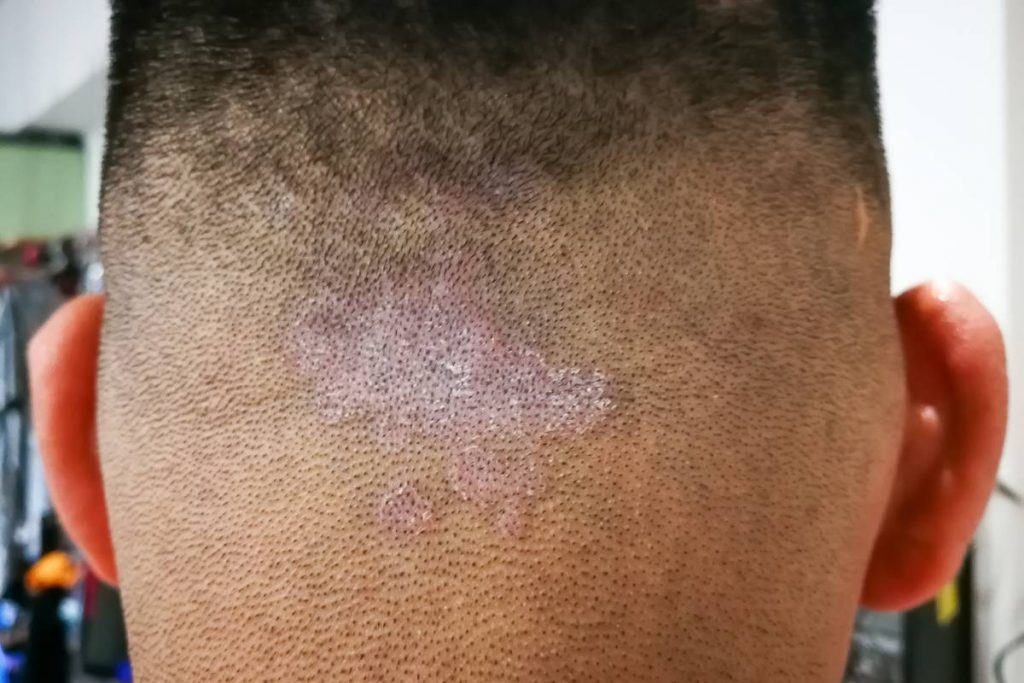
What is the main cause of seborrheic dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and flaky patches, particularly on areas of the skin rich in oil glands such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. While the exact cause is not fully understood, several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Malassezia yeast: This type of yeast is found on the skin of most adults but can cause irritation in some individuals. It’s thought that an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast may play a role in triggering seborrheic dermatitis.
- Hormonal factors: Changes in hormone levels, particularly during puberty, can contribute to the development of seborrheic dermatitis. Hormonal fluctuations may stimulate the production of oil (sebum) in the skin, providing an environment conducive to the growth of Malassezia yeast.
- Genetics: There is evidence to suggest that genetics may play a role in predisposing individuals to seborrheic dermatitis. People with a family history of the condition may be more likely to develop it themselves.
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors, such as cold, dry weather, stress, and fatigue, can exacerbate seborrheic dermatitis symptoms.
- Immune system response: An abnormal immune response may also contribute to the development of seborrheic dermatitis, although the exact mechanism is not fully understood.
Overall, seborrheic dermatitis is likely caused by a combination of these factors, rather than a single underlying cause.
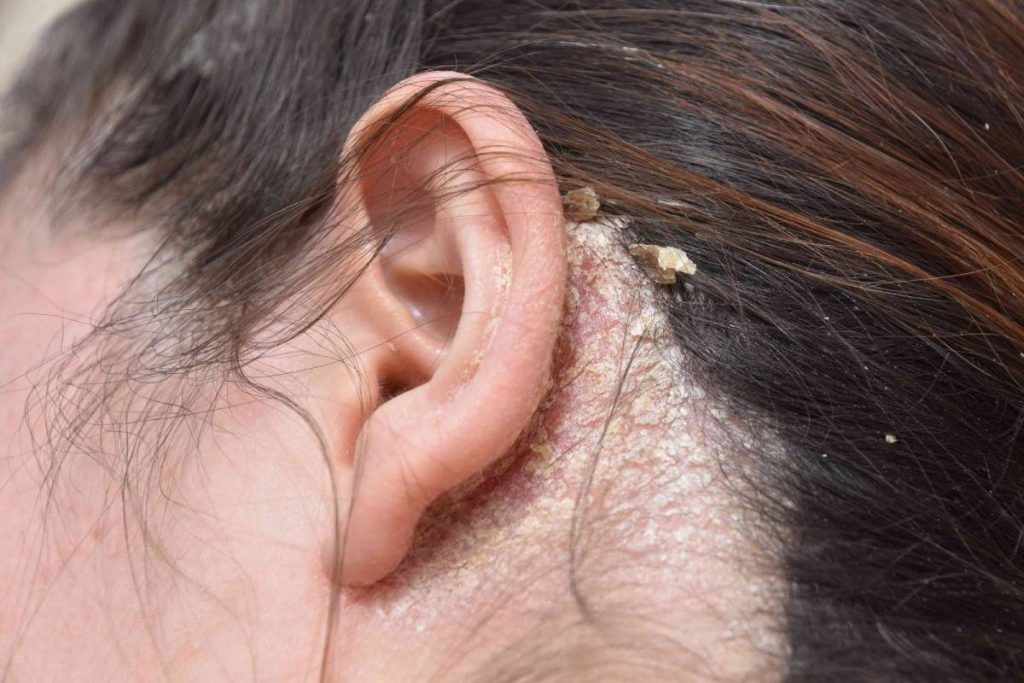
What are the common symptoms?
Common symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis can vary depending on the affected area but generally include:
- Redness: Areas of the skin affected by seborrheic dermatitis may appear red or inflamed.
- Itching: Itching is a common symptom, and it can range from mild to severe.
- Flaking: Flaky, white or yellowish scales may appear on the skin, particularly in areas rich in oil glands such as the scalp, face (especially the eyebrows, sides of the nose, and creases of the nose), ears, chest, and back.
- Greasy or oily skin: The affected areas may appear greasy or oily due to the excessive production of oil (sebum) by the skin glands.
- Scalp symptoms: On the scalp, seborrheic dermatitis can cause dandruff, with flakes of dead skin appearing on the scalp and sometimes in the hair.
- Hair loss: In some cases, particularly when seborrheic dermatitis affects the scalp, hair loss may occur, although this is usually temporary.
- Skin lesions: Seborrheic dermatitis can also present as raised, red patches with greasy scales, known as plaques, especially in severe cases.
- Sensitive or swollen skin: The affected skin may feel tender or swollen, especially during flare-ups.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis can come and go, with periods of exacerbation followed by periods of remission. The severity of symptoms can also vary from person to person. If you suspect you have seborrheic dermatitis, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan before it can get severe.
In severe cases of seborrheic dermatitis, it can weaken the skin’s immune defences, making it more vulnerable to infections. However, it’s important to note that seborrheic dermatitis itself is not a pre-cancerous condition and does not increase the risk of skin cancer.
There’s a misconception that seborrheic dermatitis causes hair loss, but this isn’t true. Hair loss is not a symptom of seborrheic dermatitis. If you’re experiencing hair loss along with skin issues, it’s likely due to another underlying condition.
Whether your severe symptoms stem from seborrheic dermatitis or another cause, it’s advisable to seek help from a qualified healthcare provider, such as a dermatologist. They can provide effective treatments to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
How is seborrheic dermatitis treated?
Treating seborrheic dermatitis depends on its severity. In mild cases, simply switching to a different shampoo might do the trick, or the condition might clear up on its own without treatment. However, if symptoms persist for more than two weeks, it’s wise to consult a healthcare provider to explore over-the-counter or prescribed treatment options. Most adults with seborrheic dermatitis require a treatment plan to manage their symptoms effectively.
Here are some tips for managing seborrheic dermatitis:
- Choose the right shampoo and skincare products: Establishing a consistent skincare routine can help control symptoms. Use a gentle cleanser containing 2% zinc pyrithione to wash affected areas daily, followed by a moisturizer. If the hairline is affected, opt for dandruff shampoo and hair products designed for sensitive skin. Look for shampoos with active ingredients like pyrithione zinc, selenium sulfide, ketoconazole 1%, tar, or salicylic acid.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Adopting healthy habits, such as stress management and adequate sleep, can benefit your skin. Stress reduction, in particular, can significantly improve seborrheic dermatitis symptoms. Try incorporating light exercise like yoga or walking, journaling, meditation, or spending time outdoors into your routine. Find stress-relief techniques that work best for you and prioritize self-care.
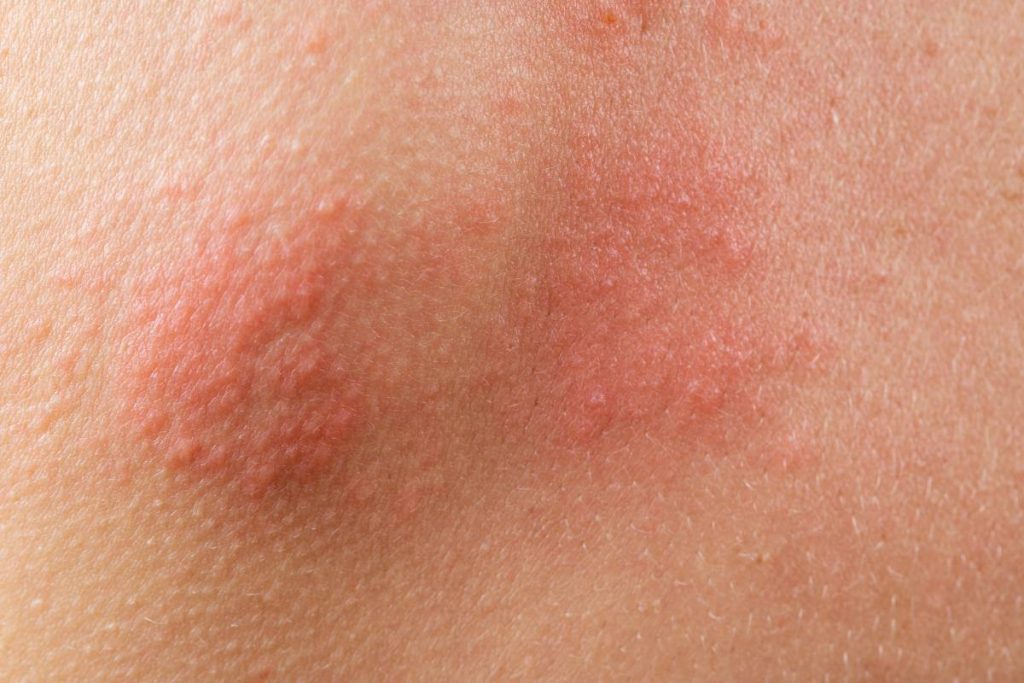
If changes in lifestyle and skincare routines don’t provide relief, it may be time to explore over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription treatments. These aim to remove scales, alleviate itching, and reduce inflammation, which causes redness and swelling in this skin condition.
For infants, a gentle approach with emollients like mineral oil or petroleum jelly can often suffice to loosen scales. However, managing seborrheic dermatitis in adults can be more complex, often requiring ongoing treatment and self-care to prevent flare-ups.
Dermatologists typically start with mild cases using topical antifungal creams or medicated shampoos, such as prescription anti-fungal shampoos or over-the-counter dandruff products. Common topical treatments include creams containing 1% ciclopirox or 2% ketoconazole. Since these ingredients may dry out the skin, it’s essential to follow up with a gentle moisturizer after application.
For more severe cases, intermittent use of topical corticosteroids like fluocinolone or additional steroids, or calcineurin inhibitors, may be necessary. Other options for severe cases may include hydrocortisone ointments or oral medications like pimecrolimus or tacrolimus.
Consulting with a dermatologist or another experienced healthcare provider in dermatology is crucial to discuss treatment options and understand the potential side effects of each.
When to seek medical advice?
If you’re considering over-the-counter or prescription treatments, it’s wise to consult a doctor to determine the best course of action. It’s also a good idea to discuss any lifestyle changes or new skincare and hair products with a healthcare provider before trying them.
Additionally, if you experience a severe flare-up or notice worsening symptoms, it’s important to see your healthcare provider promptly. Your doctor can adjust your medication dosage or recommend alternative treatment options.
Your healthcare provider may suggest a skin biopsy, where a small sample of skin is taken for laboratory analysis. This can help confirm whether you have seborrheic dermatitis or another condition, guiding the most effective treatment plan.
During your appointment, your healthcare provider may ask about:
- How long you’ve experienced symptoms and their nature
- Your past and current treatment experiences
- Whether certain treatments are covered by your insurance
- How often follow-up appointments should be scheduled to monitor your condition
Based on this information, along with a physical examination and possibly a skin biopsy, your healthcare provider can offer personalized recommendations for managing your seborrheic dermatitis effectively.
